Research
New Research on High School Teachers’ Job Satisfaction and Retention
During the pandemic, teachers’ job satisfaction hit an all-time low and there have been documented increases in teachers leaving the profession over the last three years. At the start of the 2023-2024 school year, we surveyed roughly 17,000 high school teachers across the United States to more deeply understand how satisfied they are with their jobs now, what’s driving that satisfaction (or dissatisfaction), and whether we can expect to continue to see the trend of increasing numbers of high school teachers leaving the profession post-pandemic.
The new research finds that, among the 20% of high school teachers who report being very or fairly likely to leave the profession, roughly one-third report being very or somewhat dissatisfied with their job. Research shows that job dissatisfaction is a leading indicator of leaving the profession. As depicted in the figure below, more than half of high school teachers report that Lack of student motivation (69%) and Low levels of public respect for teaching (59%) detract from their satisfaction with teaching.
Percentage of Teachers Reporting Job-Related Factors that Detract from Engagement
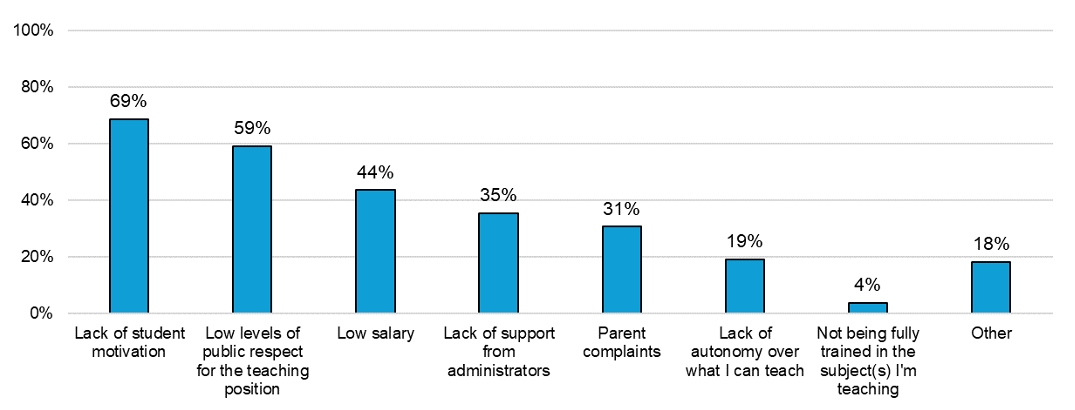
Survey question asks, “Thinking about last school year (2022-2023), what job-related factors detract from your engagement in teaching?”
The research also asks teachers to rate the overall mental health of their fellow high school teachers in the school building. Only one-third of high school teachers report that their peers have good or excellent mental health and, for those who cite poor mental health among their peer teachers, nearly 40% also report being very or somewhat dissatisfied with their job. It is perhaps not surprising that regression analyses suggest improving mental health perceptions is strongly associated with increased job satisfaction among high school teachers overall, for first-year high school teachers, and for Advanced Placement (AP) teachers.
Read the full research study here.